以ArrayBlockingQueue为例,使用如下
int BOUND = 10;//阻塞队列容量
BlockingQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(BOUND);
queue.put();//超过队列容量时则put()阻塞
queue.take();//队列容量为0时则take()阻塞初始化逻辑
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this(capacity, false);//默认非公平锁
}
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
if (capacity <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.items = new Object[capacity];
lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);//创建一把锁
notEmpty = lock.newCondition();//使用这把锁,创建条件对象
notFull = lock.newCondition();//使用这把锁,创建条件对象
}关于这三个属性,注释里很明白
/** Main lock guarding all access */
final ReentrantLock lock;
/** Condition for waiting takes */
private final Condition notEmpty;
/** Condition for waiting puts */
private final Condition notFull;/生产者put,消费者take,ArrayBlockingQueue保证同一时刻只有一个线程能操作。
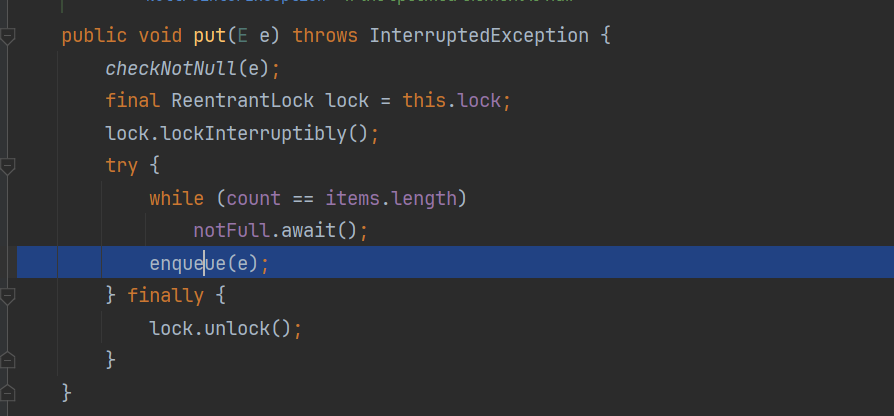
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();//以可中断方式获取锁
try {
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await();
enqueue(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();//以可中断方式获取锁
try {
while (count == 0)
notEmpty.await();
return dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}可以看出,put和take里都是先尝试获取锁,获取锁失败的线程,都会阻塞到parkAndCheckInterrupt()里:
private void doAcquireInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}此时,未获取锁的线程,已经入到CLH同步等待队列中,等待释放锁的线程调用unlock(),去唤醒CLH队首的线程。
put方法跟踪
假设此时某一个生产者线程p1获取了锁,此时执行到notFull.await();
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();//以可中断方式获取锁
try {
while (count == items.length)//判断是否队列已满,
notFull.await();//满了则阻塞
enqueue(e);//未满则将操作元素e插入blockingqueue
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}进入notFull.await()方法
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
Node node = addConditionWaiter();//入队条件等待队列
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);//完全释放锁,即使本线程多次冲入,则释放多次,state直接置为0
int interruptMode = 0;
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {//判断如果不在同步队列clh中,则需阻塞当前线程
LockSupport.park(this);//生产者线程阻塞在此处
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
}
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
if (node.nextWaiter != null) // clean up if cancelled
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
}此处先不考虑可中断的情况,await()里逻辑包括以下几方面:
1.await作为往队列插入元素前的最后一道检查,需要保证,如果队列已满,则需阻塞当前线程,且 需要释放锁,供其他消费者线程获取后,执行take(),从而降低阻塞队列的容量。
2.不管put还是take(),操作队列中元素的前提都是获取锁,所以,未获取锁的线程,不管是是生产者还是消费者,都会进入clh中,而前面p1,在await里因为blockingqueue容量满,释放锁时,唤醒clh队首的线程,此时可能是生产者,也可能有消费者。
3.假设队首线程又是生产者,则此时该线程会拿到锁,又会进入到notFull.await(),然后判断已满,继续进入条件等待队列,继续释放锁,唤醒下一个clh队首线程,
如此重复,直到遇到下一个消费者线程。
4.注意一点,只有在clh队首的线程才能获取锁,条件等待队列中的线程是没法获取锁的,因为unlock里release方法里取要unpark的线程时,就是从clh队首head取的。
take方法跟踪
下面再看消费者take方法做了什么,notEmpty.await(),
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0)//判断队列是否为空,即长度为0
notEmpty.await();//
return dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}此处逻辑完全跟put里的一样,只不过,此时移到名为notEmpy的条件等待队列当中,
接上面p1线程释放锁,经过若干生产者线程继续移到上面的notFull的条件等待队列中,终于换醒了第一个消费者线程c1,
此时c1判断count=10,即执行dequeue(),
private E dequeue() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[takeIndex] != null;
final Object[] items = this.items;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E x = (E) items[takeIndex];
items[takeIndex] = null;
if (++takeIndex == items.length)
takeIndex = 0;
count--;
if (itrs != null)
itrs.elementDequeued();
notFull.signal();//notFull发出通知,然后其他生产者可以继续往队列插入元素了
return x;
}
public final void signal() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
Node first = firstWaiter;//取notFull条件等待队列首第一个
if (first != null)
doSignal(first);
}
private void doSignal(Node first) {
do {
if ( (firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null)
lastWaiter = null;
first.nextWaiter = null;
} while (!transferForSignal(first) &&//移到sync queue
(first = firstWaiter) != null);
}
final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {
/*
* If cannot change waitStatus, the node has been cancelled.
*/
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))
return false;
/*
* Splice onto queue and try to set waitStatus of predecessor to
* indicate that thread is (probably) waiting. If cancelled or
* attempt to set waitStatus fails, wake up to resync (in which
* case the waitStatus can be transiently and harmlessly wrong).
*/
Node p = enq(node);//移动到同步队列
int ws = p.waitStatus;
if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL))
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread);//唤醒生产者线程
return true;
} 唤醒生产者线程后,线程从await()里的park处恢复,
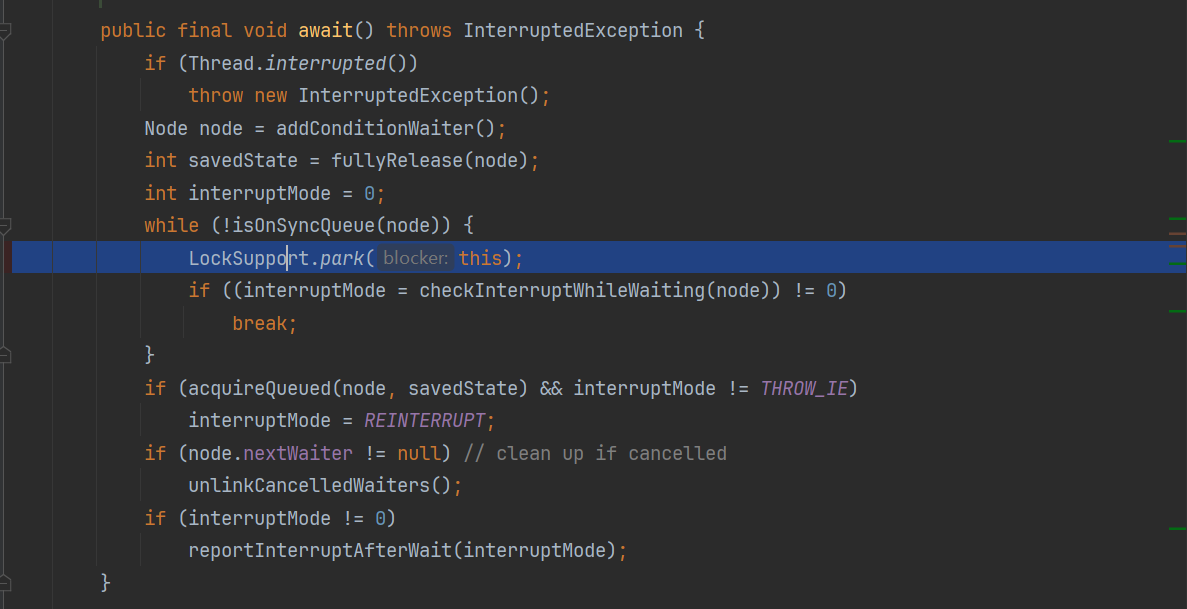 然后继续先去抢锁,
然后继续先去抢锁,
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
int interruptMode = 0;
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
LockSupport.park(this);
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
}
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)//抢到锁才继续,抢不到继续阻塞到此处
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
if (node.nextWaiter != null) // clean up if cancelled
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
}如果此时唤醒的p2线程,未在同步队列首位,则抢锁失败,又会阻塞在此。
如果抢锁成功,则往后执行,enqueue(e),插入元素。
.png)